- Diamond wheels&
CBN wheels - For Surface & Cylindrical
- For Profile grinding
- For Internal grinding
- For Tool grinding
- For Sawing & Cutting
- Diamond &
CBN Electroplated tools - Mounted wheels for internal
- Files and wheels
- Diamond &
CBN Compact tools - PCD tools
- PCBN tools
- Wear resistant parts
- Natural Dia. Cut. tools
- Diamond dressers
- Diamond hand-stones
- Other products
- Inquire
- Click Here
- Call us
- +81-3-3759-7405

Diamond & CBN wheels for profile grinding
Diamond & CBN wheels for profile grinding
The abrasive grits of profile grinding wheels
| Diamond | For grinding hard-to-machine materials such as tungsten carbide, cermet, ceramics. |
| CBN | For grinding ferrous materials such as SKH、SKD、SKS、SUS. |
| The grit size | |
| The sizes diamond and CBN belong to same standard, the selection of grits is very related to the nose width and nose radius Please refer to “The nose angle and nose strength of profile grinding wheels”of this page. |
|
| Concentration (100、125、150) | |
| In general we recommend you to choose concentration at 100 or more. | |
Types of Profile grinding wheels (by bond)
Profile grinding wheels are mainly devided into 3 types.
- Metal bond
is sinterd Metal powder with abrasives and has abundant heat and wear-resistance which makes the tool life longer to retain accuracy of the tools. - MVD.......It has excellent wear-resistance and its sharp nose or rim of wheel is strong good for the works without an operator for long hours. It is the premium bond.
- MVD-S....It is standard type of MVD bond and brings you not only good performance but also fairly good life at cheaper price.
- MKD.......At the same sizes of grits with the same concentration, it can bring you better grinding than MVD. However, nose life becomes shortened.
Nose radius>0.2 - MD ........Nose wear takes place a little quicker than MVD, but price is less than MVD for rough grinding.
- PF ........It is specially developed for thin slot grinding at high precision. Its remarkable grinding capability and excellent wear resistance can grind thin slot accurately at high precision without distortion.
- Resin bond
is sintered special resin powder. It brings you very good cutting capability for rough grinding. - RVD....... Strength of nose is slightly inferior than metal, but its cutting ability is far better. It has remarkable heat resistance, good for heavy grinding. Among resin bonds, it is the hardest bond.
- RHD....... It has best grinding ability. Depending on bonding, heavy grinding, and fabrication of thin materials are suited. It is recommended for rough grinding to finishing.
- RXD ...... In respect of heatl resistance and grinding ability, it is as good as RHD bond. But nose wear occurs a little quicker than RHD. It provides you soft grinding and suits to grind Ag-W and Cu-W.
- RD ........ It has remarkable grinding capability but wear occurs much quicker.
- RJD .......When grinding capability is first priority, this is it. It suits to grind perforated thin materials.
- Electroplated bond (P bond)
Cryston's unique electroplated bond succeeds to adhere abrasives firmly on metal cores. The bond is best recommended for profile grinding wheels which shows remarkable cutting ability.
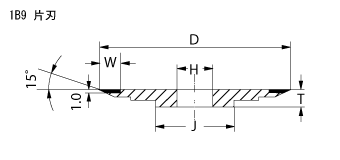
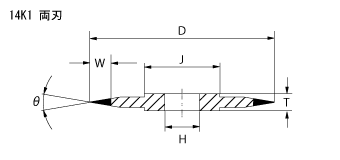
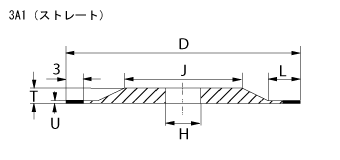
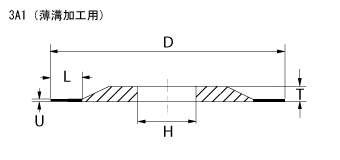
Shapes of Profile Grinding wheels
Fig1 to 3 are standard profile grinding wheels. Fig 4 is an epoc making profile wheel developed specifically to machine thin slot of tieber and punch of IC lead frame at high precision level. Demand to make the slot width narrower and depth deeper for IC frame tieber had been increased and to reply to it, we, Cryston's technical team had developed. The bond is not only highly capable in high performance, but also it makes the wheel easy to handle.
Nose angle and nose strength of Profile grinding wheels
Nose angle is available from 5°. Depending on the grit size of diamond or CBN employed, nose width and nose radius change as below. Nose strength is high at wider angle (ie an obtuse angle) , and is strong against the load given vertically, while it is weak against parallel load.
| Grit Size | 140 | 170 | 200 | 230 | 270 | 325 | 360 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1500 |
| Nose width | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| Nose radius | 0.09~ 10 |
0.08~ 9 |
0.07~ 8 |
0.07~ 8 |
0.06~ 7 |
0.05~ 6 |
0.05~ 6 |
0.04~ 5 |
0.03~ 4 |
0.03~ 4 |
0.02~ 3 |
0.015~ 2 |
Finished Surface
Depending on the grinding conditions, surface finished differs at great deal.
For instance, when you set cross feed at smaller number, particularly good surface can be achieved.
(#200MVD=0.5S/1mm/min、automatic feeding)
There are several wheels using abrasives of rough sizes. We recommend you to select a wheel depending on grinding efficiency, precision level achieved, and appearance.
| Grit size | 140 | 170 | 200 | 230 | 270 | 325 | 360 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1500 | |
| Surface roughness S |
Metal bond | 4 | 3.3 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 2 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| Resin bond | 3.3 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| Surface finished | Rough |
middle |
Precision |
Ultra precision |
|||||||||
| Workpiece=V type、peripheral speed=1500m/min、sroke=38 strokes/min、cross feed=2.4mm/min automatic feeding、depth of cut=depend on 'depth of cut ' in this page. | |||||||||||||
Depth of cut
Depth of cut dIffers from rough grinding to finish grinding and have an effect on a wheel life at great deal. Economical depth of cut are listed below.
| Grit size | 150~230 | 270~400 | 600~800 | 1000~1500 |
| Depth of cut | ~0.1~0.5 |
~0.01~0.1 | ~0.005~0.01 | 0.005 below |
Run-out
When the wheel has a bigger run-out (ie the wheel is vibrated), the active surface of the wheel becomes loaded at early stage and grinding capability is lowered quickly. Then, nose width becomes wider soon while it may cause to break the wheel. To keep the smallest run-out (below 0.005)、when you order a new wheel, please supply a new flange. Once you set the flange, please do not remove it.
Nose life of Profile grinding wheel
Nose life differs depending on how rotation no., stroke no., depth of cut, feed speed and workpiece are related,
How to us a Profile grinding wheel effectively.
- To keep the wheel vibration as small as possible, the wheel should be run-out at below 0.005 when mounting.
- Peripheral speed should be selected in the range of 1,000 to 2,000m/min.
- 90 strokes/min or below is recommended.
- The grit sizes recommended are up to #800 for practical use, for specified case #1000 of metal bond, and #1500 of resin bond. In general, abrasives of #600 are employed for finishing.
- When the wheel becomes deformed or cutting capability lowered, truing (forming) must be applied to the wheel and then dressing the wheel back to the original form.
- For handling and taking in custody, you have to treat the wheel very discreetly for its sharp edge. It applies particularly to thin wheels.
- To bring out the best performance of a wheel, change the grinding conditions many times at the machine table with workpiece until you find the condition you get the best achievement. It will be your know-how.
- When the following state occurs, check out the items on right side.
| Dull or blunt of metal core | → | Stroke inclination |
| Burning | → | Glazing |
| Chattering | → | Run-out, grit size |
| Feeding mark | → | crossfeed, depth of cut |
| Barrell finished | → | Width of stroke |