- Diamond wheels&
CBN wheels - For Surface & Cylindrical
- For Profile grinding
- For Internal grinding
- For Tool grinding
- For Sawing & Cutting
- Diamond &
CBN Electroplated tools - Mounted wheels for internal
- Files and wheels
- Diamond &
CBN Compact tools - PCD tools
- PCBN tools
- Wear resistant parts
- Natural Dia. Cut. tools
- Diamond dressers
- Diamond hand-stones
- Other products
- Inquire
- Click Here
- Call us
- +81-3-3759-7405

HOME > Diamond wheels &CBN wheels
Diamond wheels &CBN wheels
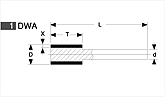
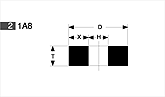
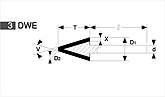
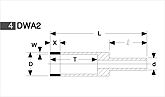
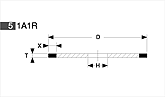
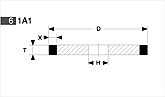
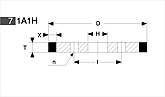
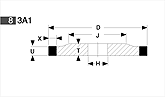
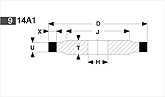
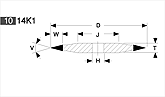
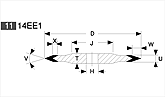
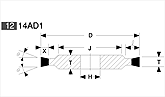
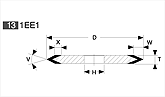
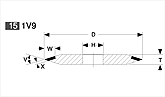
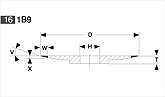
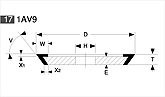
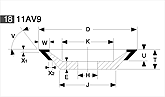
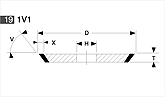
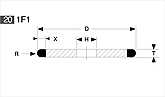
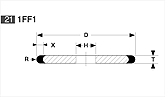
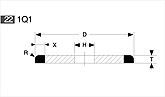
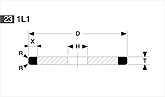
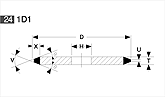
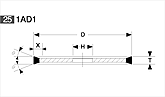
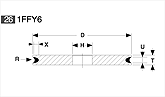
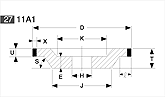
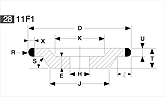
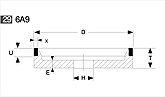
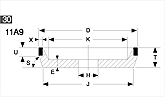
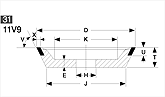
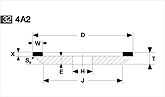
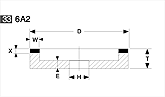
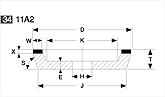
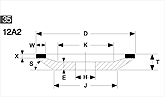
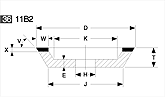
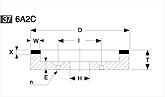
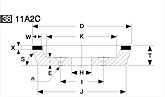
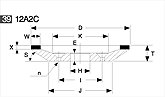
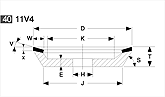
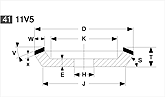
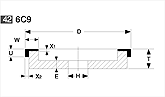
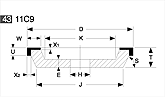
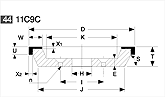
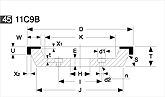
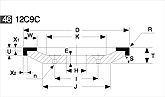
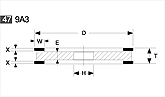
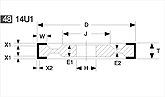
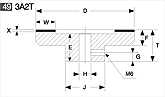
Basic shapes of wheels
*Show larger size image on click
Diamond&CBN powder

Synthetic diamond
The size of diamond particle that made the powder is considered as that of the sands.
Diamond and CBN powders are not just one type. Ther are various kinds in various types among which you can select the most adequate one to meet your purpose and machining condition.
A Wheel Structure

A wheel is made of a steel core and abrasive layer. The abrasive layer is sintered under the best condition with the best raw materials which we achieved thru our R & D works for years to meet each application. The wheel structure is marked on the wheel.
Wheel markings (engaraved on the wheel.)
On each wheel the following is indicated to show what the abrasive layer is made of.


| Dia. Types | Size | B. grade |
Conc. | Bond | Specail bond | Dia. layer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.0(mm) 1.5(mm) 2.0(mm) 3.0(mm) 4.0(mm) 5.0(mm) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What is bond for diamond wheels&CBN wheels?
Diamond and CB powders generally called 'superabrasives' are sintered together with the most adequate bond for each application to create the abrasive layer.
To select the best wheel for your work, it is necessary to select the most suitable bond to meet your purpose and grinding conditions.
| Bond | Characteristic | Main application | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R:Resin (Resin) |
Sintered special resin; sharp cutting ability is provided and most suitable for rough grinding. | RV | For profile grinding. Excellent wear and heat resistance of wheel nose or rim. | diamond For finish grinding of tungsten carbide. For heavy grinding of ferrite and stone. For formed tools of ceramics and glass. For grinding cermet ad compact tools. For combination grinding of tungsten carbide and steel. CBN For special tool steel, high speed steel carburized hardened steel, die steel Other ferrous materials |
| RH | Most suitable for heavy and rough grinding to finish grinding. | |||
| RJ | Light grindability | |||
| R | Excellent grindability | |||
| M:metal (Metal) |
Sintered metal powder provides heat and wear resistance that gives longer tool life to maintain high accuracy in finished size. | MVD | Excellent wear resistance makes the machine possible to run without an operator for a long time. | |
| MKD | Soft metal, very good grindability. | |||
| M | Conventional bond, inexpensive and good for rough grinding. | |||
| PF | For grinding thin slot at high precision. | |||
| V:Vitrified (Vitrified) |
Sintered ceramics which have adequate pores to create good grindability. | VC | Suitable for generating and grinding cutting edges of PCD cutting tools and good for wear resistant parts. | |
| V | Strong to hold grit and good to cut make it suitable mainly for hand-stone to grind cutting edges of engraving tools. | |||
| P:Electroplated (Electroplated) |
The method provides 2 to 3 times longer life than the conventional ones. | P | Complicated shapes can be machined. Cost saving. |
|
※(D)= dry type.